
A team of researchers led by Prof. SHAO Dingfu from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with Prof. XIAO Ruichun and Prof. LI Hui from Anhui University, have identified a unique phenomenon, known as the "skin effect," in the nonlinear optical responses of antiferromagnetic materials.
The research, published in Physical Review Letters, provides new insights into the properties of these materials and their potential applications in advanced technologies.
Nonlinear optical effects occur when light interacts with materials that lack inversion symmetry. Traditionally, it was believed that these effects were uniformly distributed throughout the material. However, the research team discovered that in antiferromagnets, the nonlinear optical response is concentrated on the surfaces, similar to the "skin effect" seen in conductors, where currents flow primarily on the surface.
To investigate these nonlinear optical responses in antiferromagnets, the team developed a computational method, using the bulk photovoltaic effect as a representative example. Their results showed that, while the global inversion symmetry was broken, the local inversion symmetry deep inside the antiferromagnet remained largely intact. As a result, the nonlinear optical response was primarily confined to the top and bottom surfaces, with negligible contribution from the material's interior.
To validate their findings, the researchers conducted first-principles calculations on the two-dimensional antiferromagnet CrI3, confirming the surface-dominant behavior of the bulk photovoltaic effect. They also calculated the second-harmonic generation effect, which aligned consistently with their theoretical models.
The discovery of the skin effect in nonlinear optical responses opens exciting opportunities for both fundamental science and optoelectronic technology. "It offers a new perspective on how nonlinear optical effects can be utilized in high performance device applications," said Prof. SHAO.
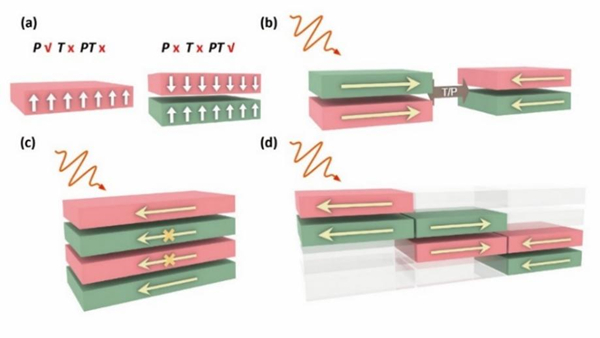
Schematics for the skin effect of the bulk photovoltaic current (Image by SHAO Dingfu)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

